Welcome back! The AI ecosystem is starting to hit limits that feel structural rather than technical. Companies are pushing for more capacity than the grid can deliver. Models are shaping conversations faster than people can verify them. Creative platforms are discovering that synthetic content can overwhelm a culture overnight.
In today’s Generative AI Newsletter:
• Google faces a six-month doubling cycle for AI capacity
• Pinterest users push back against AI generated feeds
• QUT researchers map how chatbots handle conspiracy content
• OpenAI releases GPT 5.1 Codex Max for long horizon coding
Latest Developments
Google told employees it faces an unusual crisis of scale. At an all-hands meeting, Google’s AI infrastructure head told employees the company must double serving capacity every six months and reach a thousandfold increase within five years. The growth curve is colliding with power limits, chip shortages, and the sheer weight of AI features being pushed into Search, Gmail, Workspace, and the Gemini app. If Google cannot scale fast enough, the next wave of AI products will hit hard limits before they reach the public.
What’s happening?
Internal target: Google leadership set a goal to increase serving capacity by a thousandfold within five years while keeping power and cost nearly flat.
Supply bottlenecks: NVIDIA chips remain sold out as demand grows, restricting how fast Google can roll out new AI features.
Custom silicon: Google is leaning on its Ironwood TPU, which it says is far more power efficient than earlier generations.
User pressure: Several AI products, including Veo, launched to strong interest but could not reach more users due to compute shortages.
Google is racing competitors in a moment when models improve faster than infrastructure can follow. The company is betting that building its own chips, expanding its data centers, and squeezing more efficiency out of every system will be enough to stay ahead. Google executives acknowledged employee concerns about an AI bubble, but they also called 2026 an intense year ahead as cloud demand, infrastructure expansion, and model rollouts stack on top of each other.
Special highlight from our network
AI That Keeps Your Brand Performing Everywhere
Ever tried keeping hundreds of business listings accurate and on-brand?
It’s chaos.
One outdated link or unanswered review can instantly hurt trust.
That’s why Uberall built UB-I:
an AI agent that updates listings, responds to reviews, and boosts engagement across every channel.
No waiting. No manual cleanup. Just consistent visibility at scale.
What’s the hardest part of managing local presence?
Try UB-I

Pinterest is being reshaped by AI generated images, shopping ads, and a strategy that its most loyal users say feels nothing like the app they grew up with. The shift began after CEO Bill Ready recast Pinterest as an AI powered visual shopping assistant, framing it as part of the new retail race alongside Google, Amazon, and OpenAI. That vision is now colliding with real user frustration as searches produce one eyed cats, impossible recipes, and photo feeds overwhelmed by synthetic content.
What users are reporting:
Search quality collapses: Users described seeing distorted animals, broken foods, and uncanny images in categories that used to be reliable.
Creative community backlash: Artists and designers told CNN they no longer recognize the app and worry their work is being scraped or imitated.
AI controls fall short: Pinterest released an AI “tuner” and widespread labels, yet users say the tool cannot keep pace with daily uploads.
Shift toward shopping: Half of Pinterest’s 600M monthly users are Gen Z, and the company now prioritizes AI powered product discovery and ad clicks.
The company wants to turn searches into purchases. The community wants to protect the space that helped them think, plan, and create. Platforms that built their value on human creativity cannot simply inject automation and trust the culture to adapt. Communities are fragile, and identity is earned through years of consistent behavior. Pinterest’s evolution is a warning flare for every AI product team. AI can accelerate discovery and commerce, yet it can also erode the qualities people came for if deployed without sensitivity to the culture already in place.

New peer reviewed research from Queensland University of Technology’s Digital Media Research Centre shows that today’s major chatbots often engage with conspiracy theories instead of shutting them down. The study used a “casually curious” persona asking common questions about nine conspiracies, from the JFK assassination to recent election falsehoods, and found that several systems offered speculation, presented misinformation next to facts, or softened their refusals.
What researchers observed:
Loose handling of older myths: Every chatbot entertained discussion of JFK assassination conspiracies, often pairing false claims with legitimate background in the same reply.
Tight restrictions on hate topics: Models showed stronger protections on prompts tied to antisemitism, race based claims, or the Great Replacement Theory.
Clear model differences Perplexity: provided sourced answers and discouraged misinformation, while Grok Fun Mode joked through topics and described conspiracies as “more entertaining.”
Political refusals Google Gemini: declined prompts about 2024 election claims, birth certificate rumors, and other fresh political narratives, redirecting users to Search.
The researchers warn that even “harmless” myths create a psychological on-ramp to more extreme beliefs. Their data shows that interest in one conspiracy raises susceptibility to others by conditioning distrust of institutions and normalizing speculative reasoning. The risk now sits inside everyday tools on people’s phones. A casual question at a barbecue can quickly turn into a guided tour of ideas that should never carry an academic tone.

GPT 5.1 Codex Max is OpenAI’s new coding model built for tasks that stretch far beyond a single file or a single prompt. It handles multi-hour refactors, long debugging cycles, and complex agent loops by compacting its own context while it works. This lets it keep track of a project even when the token count explodes, something regular models struggle with.
Core functions:
• Session compaction: Preserves important context so the model can continue through very long tasks without losing track of previous steps.
• Long-running work: Designed for workflows that run for hours, including multi-file refactors, CI failures, and deep debugging.
• Token efficiency: Uses fewer thinking tokens while maintaining strong reasoning quality, improving reliability in big projects.
• Agentic execution: Works with the Codex CLI and IDE agents to open files, run tests, apply patches, and iterate without manual prompting.
• Windows support: Works on Windows for the first time in Codex workflows, opening access for a larger group of developers.
Try this yourself:
Give Codex Max a real project task. Ask it to plan a refactor, apply patches, run tests, and fix failures. Let it run for multiple iterations. Pay attention to how well it remembers failing tests, preserves context, and continues the workflow without being reminded.
Refactor task example: “Refactor the payment/ module to extract payment processing into payment/processor.py. Keep public function signatures stable for existing callers. Create unit tests for process_payment() that cover success, network failure, and invalid card. Run the test suite and return failing tests and a patch in unified diff format.”
GPT 5.1 Codex Max is OpenAI’s new coding model built for tasks that stretch far beyond a single file or a single prompt. It handles multi-hour refactors, long debugging cycles, and complex agent loops by compacting its own context while it works. This lets it keep track of a project even when the token count explodes, something regular models struggle with.
Core functions:
• Session compaction: Preserves important context so the model can continue through very long tasks without losing track of previous steps.
• Long-running work: Designed for workflows that run for hours, including multi-file refactors, CI failures, and deep debugging.
• Token efficiency: Uses fewer thinking tokens while maintaining strong reasoning quality, improving reliability in big projects.
• Agentic execution: Works with the Codex CLI and IDE agents to open files, run tests, apply patches, and iterate without manual prompting.
• Windows support: Works on Windows for the first time in Codex workflows, opening access for a larger group of developers.
Try this yourself:
Give Codex Max a real project task. Ask it to plan a refactor, apply patches, run tests, and fix failures. Let it run for multiple iterations. Pay attention to how well it remembers failing tests, preserves context, and continues the workflow without being reminded.
Refactor task example: “Refactor the payment/ module to extract payment processing into payment/processor.py. Keep public function signatures stable for existing callers. Create unit tests for process_payment() that cover success, network failure, and invalid card. Run the test suite and return failing tests and a patch in unified diff format.”
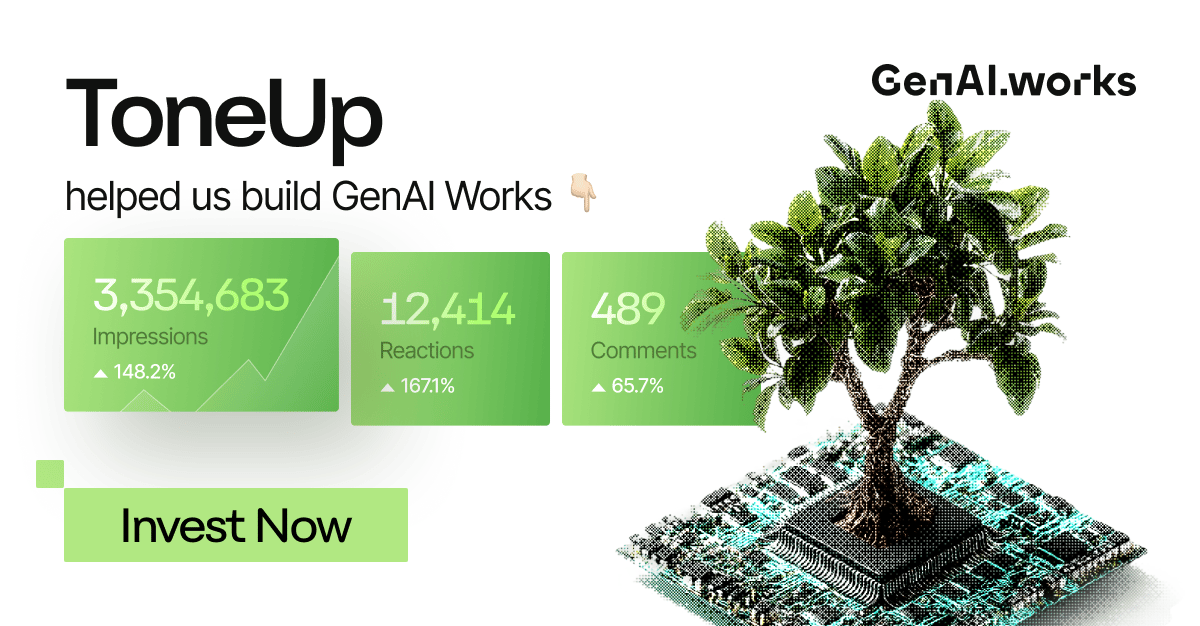
Creating powerful content shouldn’t require jumping between tools.
ToneUp centralizes your workflow, strategy, drafts, posts, voice matching, visuals and editing, all inside one workspace designed for speed and consistency.
What once powered our own content engine is becoming a product for everyone ready to scale their presence.
Support GenAI Works as we introduce ToneUp to the world.
Reg CF offering via DealMaker Securities. Investing is risky.